Have you noticed that even small amounts of caffeine can affect your sleep cycle and quality? This article analyzes the relationship between caffeine and sleep in depth. From how caffeine affects deep sleep and the REM stage, to how to optimize when you drink it to protect Sleep Hygiene. Check out this article to understand how to determine a safe dose of caffeine, the best time to take it, and suggest alternatives to stay awake without affecting the quality of your sleep.
Does caffeine affect how you sleep?
Caffeine has a major impact on the sleep cycle by reducing sleep time and disrupting the REM cycle, especially near bedtime. How caffeine and alcohol affect your sleep: Many studies show that caffeine also increases sleep onset time and prolongs the pre-sleep stage, leading to reduced sleep quality.
Humans consume caffeine daily, which easily affects the circadian rhythm and melatonin levels that can be recorded. Often leads to difficulty sleeping and waking up in the middle of the night in many people. Clinical and epidemiological evidence suggests a link between caffeine and its ability to cause decreased sleep performance. At the same time, it increases alertness and also affects the ability to concentrate the next day.
Does Your Afternoon Coffee Steal Your Sleep?
Can Caffeine Cause Insomnia?
Caffeine use can increase insomnia symptoms in many people, especially when taken close to bedtime or used in high doses. In some studies, drinking coffee before bed in amounts of 400 mg of caffeine 0, 3, or 6 hours before bed may reduce sleep onset time. At the same time, it increases wakefulness time and affects overall sleep quality. Although there may be an influence between caffeine sensitivity, age and caffeine tolerance. However, high sensitivity to caffeine is the main cause of difficulty falling asleep and disrupting sleep, which can last until the next morning.
Read more: Why do we need sleep
How long will caffeine keep me from sleeping?
The time it takes caffeine to affect sleep varies depending on each person’s tolerance threshold and sensitivity. Some scientific studies show that caffeine use can cause sleep disruption, prolong the time it takes to fall asleep, and they can last up to several hours after drinking.
So, how long caffeine and sleep affect each other. The time it takes for the body to eliminate half of the caffeine is about 3 – 5 hours in healthy adults. However, in some people, it can last up to 7 – 9 hours, but it depends on genetic factors and the level of liver elimination. Therefore, to minimize negative effects, you should limit caffeine use in the afternoon or late evening. In particular, you need to consider your health condition to develop a plan to consume a reasonable amount of caffeine.
Read more: How Many Hours of Sleep Do We Really Need?
Is Caffeine Good or Bad for Health?
On the other hand, caffeine helps increase alertness, maintain concentration, and improve cognitive performance. It is also considered a substance that enhances metabolism and athletic performance in some people.
However, if you consume too much caffeine, the downside will appear: it can cause anxiety, heart palpitations, a temporary increase in blood pressure, and especially negatively affect sleep and work efficiency the next day. Many studies have shown that caffeine can disrupt the melatonin cycle and reduce the quality of deep sleep. From there, it affects the function of helping the body stay awake during the day.
Therefore, we need to balance caffeine and deep sleep. Because this decision needs to be based on benefits and risks. At the same time, it must be consistent with each individual’s sleeping habits and health goals.
Read more: Why can’t you sleep? The link between sleep and anxiety
How Much Caffeine Is Safe To Drink?
A safe dose of caffeine for healthy people is usually recommended by sleep therapists to be about 200–400 mg a day. But the dosage may vary depending on each person’s specific health condition.
However, to ensure deep sleep and minimize the risk of insomnia, many sleep therapists recommend limiting both the amount and duration of caffeine consumption. So how late can you have caffeine and still sleep. People who are prone to insomnia or have poor sleeping habits should completely avoid caffeine within 6 hours before bed.
For people sensitive to caffeine or children, strict limits are necessary, and certified sleep coaches should be consulted before using any caffeine-containing products. In particular, pay attention to your total daily consumption, because caffeine is not only found in coffee but also in tea, chocolate, and energy drinks.
Read more: How to Build a Healthy Bedtime Routine for Better Sleep
Tips to Drink Coffee Without Affecting Your Sleep
Understanding the relationship between caffeine and sleep will be the foundation to help maintain deep sleep and can be used today. Here are simple rules to help you manage your caffeine consumption well:
– Determine when to stop drinking: Limit caffeine intake after the afternoon, stop before 2:00 p.m. –4:00 p.m. This gives your body enough time to metabolize before you go to bed.
– Monitor your tolerance dose: Maintain a moderate amount of caffeine in your body, and actively monitor its impact on your sleep cycle. You can use a diary or sleep tracking apps to record it.
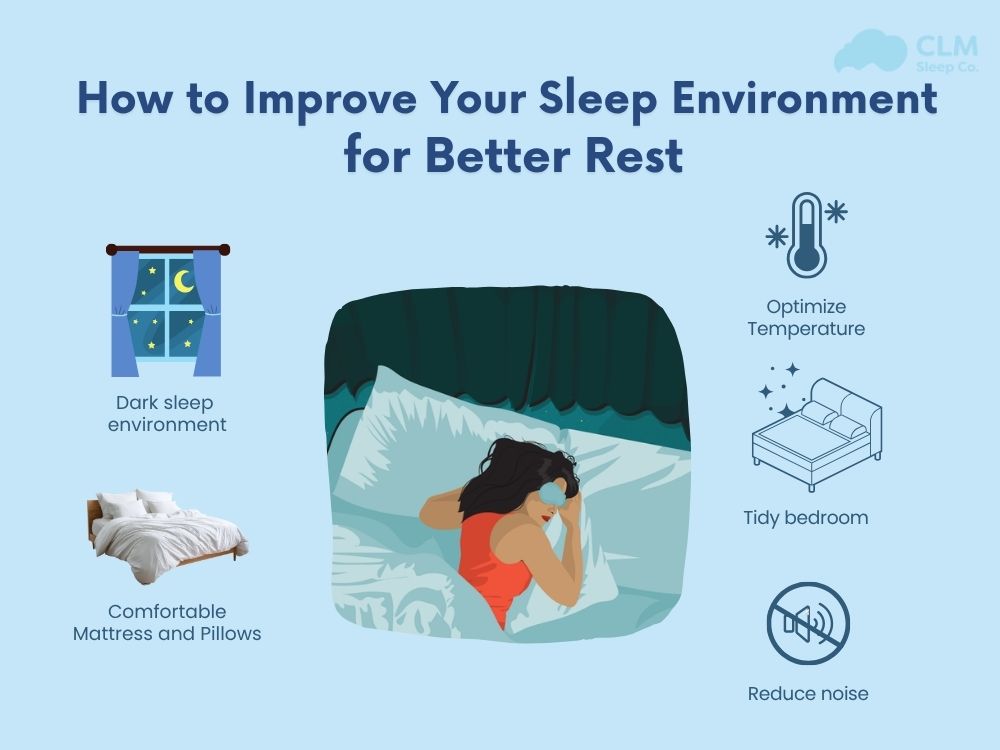
– Maintain sleep hygiene: In addition to controlling caffeine intake. Make sure your body is exposed to sunlight, have a quiet sleeping environment, and limit electronic devices before bed.
– Find alternatives: Prioritize non-caffeine or decaf food options. You can also use warm milk before bed to relax your body.
– Combined with food: When drinking coffee or drinks containing caffeine. You can eat it with food to help slow the absorption of caffeine.
5 Tips to Sleep Better
Best Caffeine Alternatives to Stay Awake Naturally
If you are looking for a solution to maintain alertness without negatively impacting deep sleep at night, especially caffeine and REM sleep. The following methods will help you maintain energy and focus in the most natural way:
- Always make sure your body drinks enough water to avoid fatigue due to dehydration, a common reason why you turn to caffeine.
- Do short exercises or light movements mid-day to increase alertness. This activity will help you feel refreshed without affecting the quality of your sleep at night.
- Take advantage of natural light and daylight, limit blue light. This helps regulate the body’s circadian rhythm and naturally increases alertness.
- Apply some relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, short meditation, or body relaxation exercises. This is one of the effective ways to boost energy without the help of caffeine.
Why Am I So Sensitive to Caffeine?
Each person’s sensitivity to caffeine is governed by many different factors. Including genetics, age, and liver function. People with long caffeine half-lives will suffer more from both sleep and alertness levels.
This is quite important when considering the relationship between caffeine and sleep deprivation. Because consuming caffeine can create a vicious cycle. The best way to limit this problem is to carefully monitor your body’s reaction after each drink. At the same time, adjust the dosage to the most suitable level to maintain healthy sleep. This requires even more attention if you have an underlying medical condition or use medications that can interact with caffeine.
What We Can Learn About Caffeine and Sleep
Deep sleep plays an essential role in brain recovery and maintaining overall health. To improve rest quality, it’s important to manage caffeine timing and dosage, while prioritizing natural ways to stay alert during the day. The guidance in this article is based on comprehensive research into how caffeine affects the body and nighttime recovery. If you are experiencing related issues, please contact CLM for a free consultation with our sleep therapists.