Deep sleep plays a crucial role in restoring health, enhancing long-term memory, and protecting the body from diseases and strokes. However, many adults today struggle to reach this stage due to work-related stress, electronic device usage, and stimulant abuse. Understanding how much deep sleep is normal can help you better manage your sleep cycle. In this article, sleep therapists explain the different stages of sleep and share practical tips to improve the quality of your deep sleep.
How about Deep Sleep
How much deep sleep should I have? It’s a question sleep therapists frequently hear from people struggling with their sleep. This is because deep sleep is crucial for both physical and mental restoration.
What is Deep Sleep?
Deep Sleep, also called slow-wave sleep or N3, is considered one of the important stages in the normal sleep cycle of each person. How much deep sleep should you have a night? A complete sleep cycle includes 4 stages:
- Stage N1: Usually light sleep, easily awakened.
- Stage N2: Medium sleep state, usually accounts for the majority of total sleep time.
- Stage N3: Deep sleep stage and hard to be awakened, this is when the body is recovering the most strongly.
- REM stage: This is the stage when the brain is most active and most dreams occur. REM sleep is important to processing emotions and strengthening memory.
This sleep cycle information will help you understand how much deep sleep you should get and what stage of sleep you are in. This makes it easier to adjust your pre-sleep habits for quality deep sleep.

Deep sleep is a solid foundation for maintaining health.
Role of Deep Sleep
- Physical recovery: Stage N3 helps regenerate cell tissues, develop muscles, bones, and enhance the immune system in the body.
- Reduce memory decline: Having deep sleep helps the brain process faster and store information more effectively and increases long-term memory capacity.
- Emotional stability: Slow-wave sleep also supports emotional balance, reducing the risk of anxiety and depression.
- Control disease risk: Prolonged deep sleep deprivation easily leads to obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
How Much Deep Sleep is Normal for Adults
The duration of a deep sleep cycle in adults is neither as prolonged as in children nor as brief as in the elderly. For a clearer understanding of the total deep sleep needed for an ideal rest at various ages, please refer to the information below.
How much deep sleep do you need by age? For adults, the slow-wave sleep cycle accounts for about 13-25% of total sleep time each night. Usually, if you sleep 7 to 9 hours, the ideal deep sleep amount will be from 1.5 to 2 hours per night.
| Age Group | Total Sleep/Night | Ideal Deep Sleep |
| Children (6 – 13 years old) | 9 – 11 hours | 2 – 3 hours |
| Teenagers (14 – 17 years old) | 8 – 10 hours | 1,5 – 2,5 hours |
| Adults (18 – 64 years old) | 7 – 9 hours | 1,5 – 2 hours |
| Seniors (65+ years old) | 7 – 8 hours | 1 – 1,5 hours |
Deep sleep average Australia: A survey in Australia showed that 57% of adults sleep 6-8 hours per night, but not everyone achieves optimal deep sleep due to modern lifestyle and work pressure.

Factors Affecting Deep Sleep
What affects deep sleep? Factors such as age, lifestyle, and health conditions often significantly affect each person’s sleep cycle. Therefore, avoid the following conditions to ensure sleep quality and bring long-term benefits to overall health.
The deep sleep stage is susceptible to many factors
Age
- The older you get, the less slow-wave sleep you have: older adults usually only get 1 to 1.5 hours of deep sleep per night. While children and teenagers may have more.
- Lack of deep sleep leads to memory decline risk: According to research in Australia, each 1% decrease in slow-wave sleep per year, usually appearing after age 60, increases the risk of Dementia by 27%.
Lifestyle
- Habits: Using electronic devices before sleep, working at night, lack of exercise, or unhealthy eating all reduce deep sleep quality.
- Exposure to blue light: Light from phones and computers causes melatonin suppression, reducing the ability to enter deep sleep.
- Diet: Eating a lot of fiber and vitamins, limiting caffeine and alcohol, helps increase deep sleep.
Health conditions
- Sleep disorders: Sleep apnea, insomnia, and restless leg symptoms all reduce deep sleep.
- Chronic diseases: Obesity, diabetes, chronic stress, and neurological diseases (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s) negatively affect deep sleep.
- Medications and stimulants: Some medications, caffeine, and nicotine disrupt the deep sleep cycle.
Signs You’re Not Getting Enough Deep Sleep
If you are experiencing the signs listed below, your body is warning about your health condition.
- Feeling tired and lacking alertness in the morning.
- Reduced ability to concentrate, remember, or learn, impaired memory.
- Often irritable and mood swings.
- Craving sweets and uncontrolled weight gain.
- Weakened immune system, easily susceptible to dangerous diseases.
- Body aches, slow recovery after physical activity.
- Sleeping a lot but still feeling sluggish.
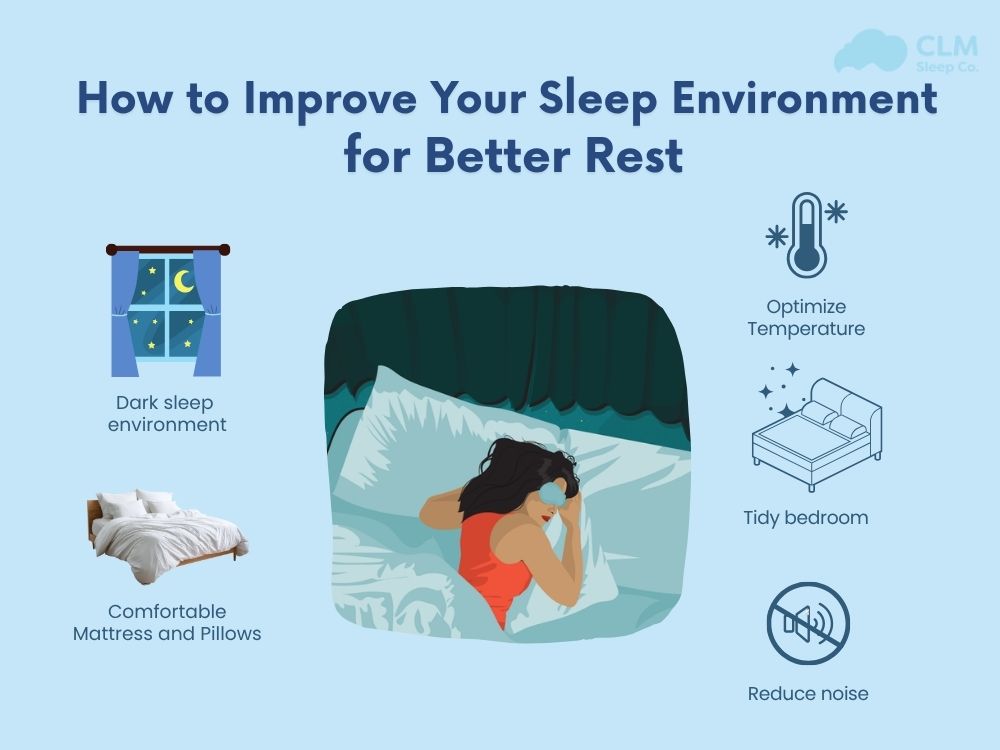
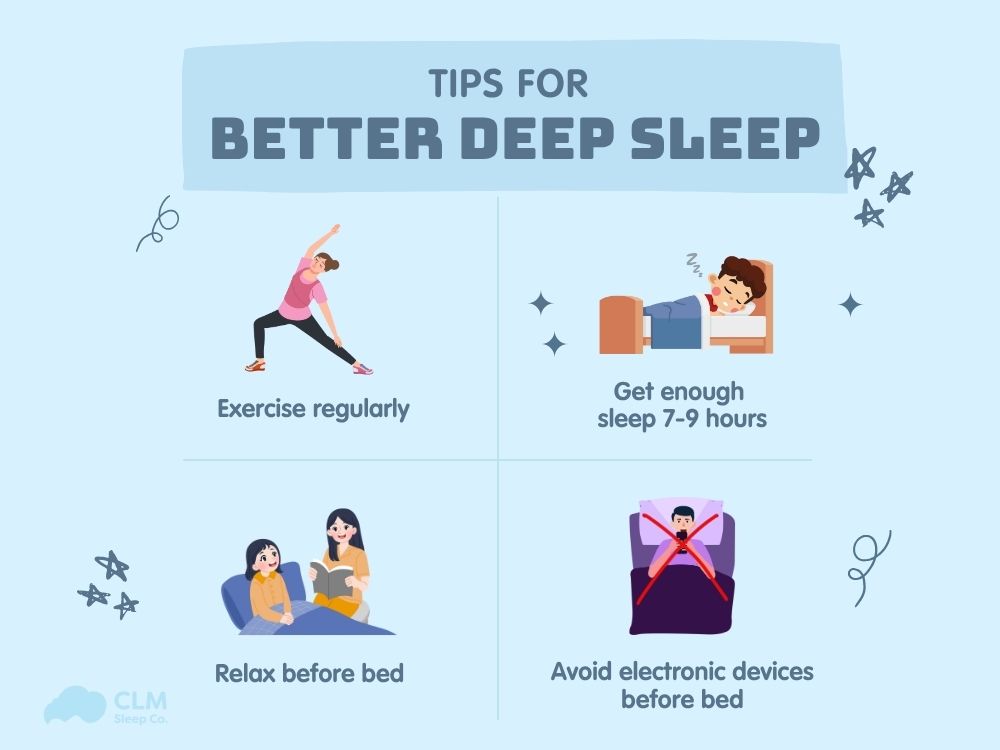
Tips to Improve Deep Sleep
How to get more deep sleep and optimize the amount of deep sleep each night? Don’t ignore the tips below recommended by certified sleep coaches at CLM Sleep to help you have quality sleep and a healthy body.
Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity helps increase deep sleep time and should be done at least 2 hours before bedtime to avoid overstimulation. Gentle exercises such as walking, yoga, or cycling in the morning or late afternoon are suitable for supporting sleep.
Get enough sleep 7-9 hours: Ensure the best total sleep time so the body can have enough deep sleep cycles. Sleeping too little or too much both negatively affect slow-wave sleep quality.
Create a relaxing routine before bed: Relaxation helps the brain enter deep sleep more easily, such as reading, listening to soft music, meditating, and taking a warm bath. Establishing a pre-sleep routine helps the biological clock operate stably.
Do not use electronic devices and avoid blue light before sleep: Blue light suppresses melatonin, reducing deep sleep quality. Turn off electronic devices at least 30 minutes before bed; prioritize a dark, quiet space.
Do not drink stimulants such as tea, coffee, beer, or alcohol before sleep: Caffeine and alcohol both reduce deep sleep time and disrupt sleep. Limit stimulants after 4 p.m. and prioritize water or light herbal teas.
See more: How to Get More REM Sleep Naturally
Conclusion
Healthy sleep pattern adults are from 1.5 to 2 hours of deep sleep each night, accounting for about 20 to 25% of total sleep time. Therefore, to achieve this optimal sleep duration, you must maintain a healthy lifestyle, manage stress, and build scientific sleep habits. If you are having difficulties with your sleep cycle, contact certified sleep coaches for in-depth consultation and personalized treatment solutions.