Sleep plays a very important role in maintaining and developing brain functions. Sleep and brain function have a close relationship in supporting memory recovery, emotional balance, and protecting the brain from the risks of cognitive decline. Throughout each sleep, the brain is responsible for performing self-repair processes and eliminating toxins to help keep the brain in a healthy state. Strengthening sleep habits not only helps improve quality of life but also helps brain function more effectively every day.
Why Sleep Is Important for Brain Health?
Sleep plays an essential role in maintaining brain health and cognitive function. Every time you sleep, the brain not only rests but also performs many important recovery processes such as repairing cells, eliminating free radicals, and limiting brain inflammation. Therefore, the brain needs to rest at night to help balance its activities after many hours of continuous work. Because without enough and quality sleep, brain activities such as concentration, memory, and reaction will significantly stagnate.
According to medical research, people who sleep less than 7 hours per night have an increased risk of neurological impairment. At the same time, the ability to learn is reduce,d and the ability to process information is limited. Therefore, sleep and brain function have an inseparable relationship that protects and develops long-term brain health. Supports maintaining clarity and creative thinking ability.
The Brain During Sleep: What Happens?
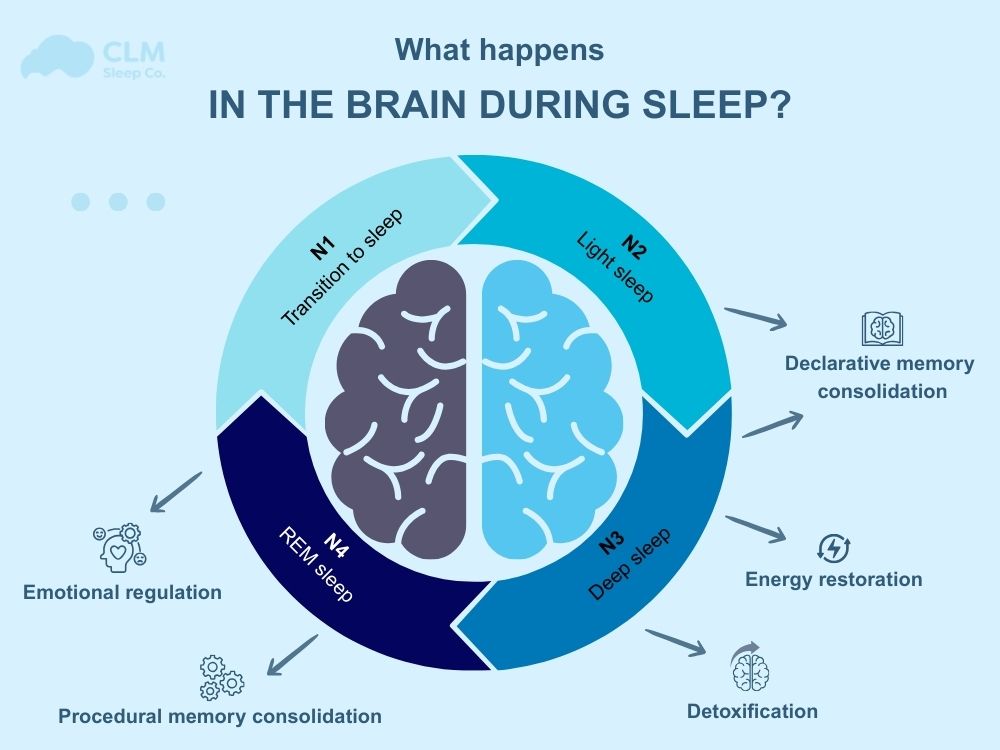
Sleep is a complex physiological process consisting of many different stages. There are 2 main stages: NREM (Non-Rapid Eye Movement) and REM (Rapid Eye Movement). Each stage will play a separate important role to help protect and restore brain function. The following content will help you understand an overview of the stages of sleep.
| Sleep stage | Characteristic | Key role in the brain |
| NREM (Non-Rapid Eye Movement) | Includes many different phases. The deepest phase is Slow Wave Sleep (SWS), the eyes cannot move quickly and the brain operates at low frequencies. | During the NREM phase, especially SWS, the brain will focus on repairing small damages on synapses – the connections between nerve cells. This process helps keep the neural network operating effectively, limiting overload or nervous breakdown.An important process that occurs primarily in NREM is the glymphatic system. They are activated to eliminate toxic substances that accumulate in the brain such as amyloid-beta. This is a metabolic product known to cause Alzheimer’s when accumulated over a long period of time. |
| REM (Rapid Eye Movement) | In this stage, the eyes move rapidly under the eyelids, the brain is often active, almost like when awake, but the body is temporarily paralyzed. | During the REM stage, the brain is often very active, continuously processing emotions and information just received during the day. The brain also filters out unnecessary information and maintains important memories in long-term memory. This process not only helps improve learning ability but also helps regulate emotional reactions and create mental balance. |
How does sleep affect your brain?
Sleep is not only the time when the body rests, but also the time when the brain performs many important functions. The close connection between sleep and brain functions shows that sleep quality directly affects all activities of each person. Below are the main mechanisms of sleep that impact brain function.
What Happens to Your Brain When You Sleep?
Sleep and Memory Consolidation
Sleep helps transfer information from short-term to long-term memory through the process of memory consolidation. During the NREM phase, the hippocampus reactivates neural patterns, supporting long-term storage of information. REM also helps enhance learning ability by maintaining emotional memory and creativity. Therefore, lack of sleep will reduce memory ability, and negatively impact learning and work results.
Sleep and Emotional Regulation
Sleep has a major impact on the ability to regulate emotions and handle stress. Insomnia often reduces activity in the frontal cortex. And the body’s emotional control center, leading to irritability, anxiety and depression. The REM phase contributes to emotional adjustment and supports mental recovery after stress. Therefore, sleep and brain function play an indispensable role in mental health.
Read more: Why can’t you sleep? The link between sleep and anxiety
Poor Sleep and Cognitive Impairment
Prolonged poor sleep can easily lead to decreased attention, slow reflexes and the risk of language disorders. This will significantly reduce work performance and learning efficiency. Some studies show that lack of sleep also increases the risk of Alzheimer’s and other degenerative neurological diseases due to the accumulation of many toxins in the brain. Always ensuring quality sleep is an important factor to protect a healthy brain.
Neuroprotective Aspects of Sleep
Sleep also plays a neuroprotective role by reducing brain inflammation and stimulating nerve cell regeneration. In particular, the glymphatic system during sleep helps eliminate toxins accumulated in the brain. Supports the nervous system to repair itself and prevent premature degeneration. This is one of the reasons why sleep and brain function is considered a natural mechanism to “renew” the brain every night.
How Much Sleep Do You Need for Brain Health?
According to medical recommendations, adults need 7 to 9 hours of sleep every night to keep their brains healthy. Children and teenagers need more sleep. While the elderly will need to pay attention to sleep quality rather than the number of hours they sleep at night.
Because deep sleep, with enough REM sleep and NREM stages, really helps restore and maintain brain function. Irregular sleep or lack of sleep every night often impairs learning, memory and emotional performance. Therefore, maintaining a stable and quality sleep schedule is an important factor for healthy brain function.
Read more: How many hours of sleep do we need?
Tips for Better Sleep and Brain Function
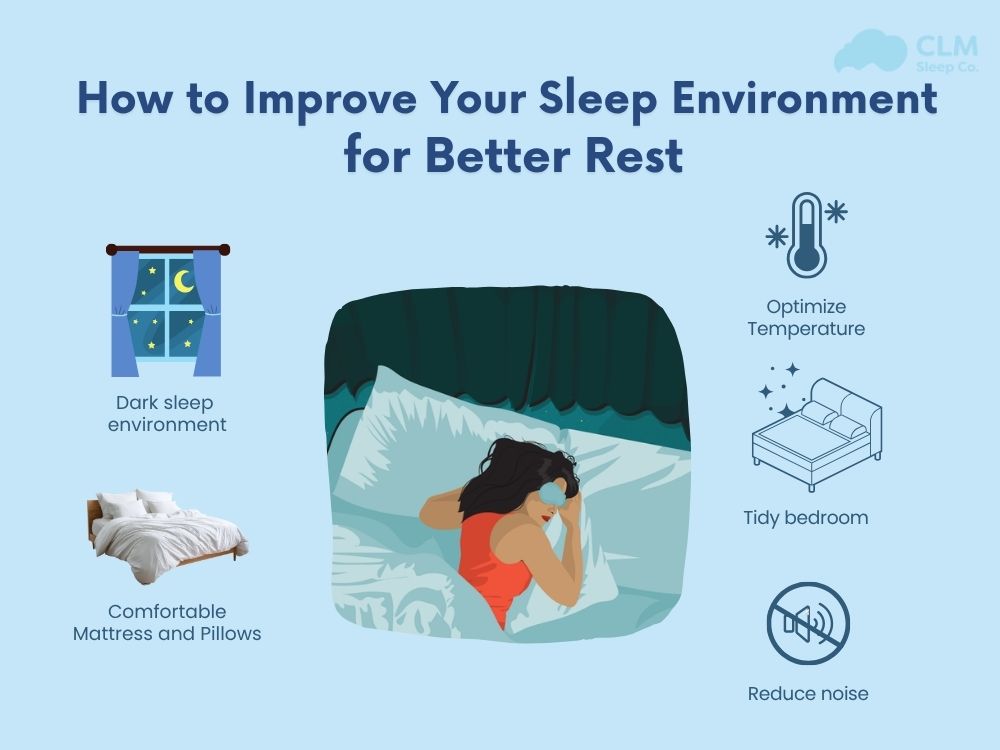
With the goal of improving sleep and brain function. Certified sleep coaches encourage effective sleep hygiene habits. This includes creating a quiet, dark, and airy sleep environment. At the same time, you should not use electronic devices 30 to 60 minutes before bed to limit blue light’s impact on melatonin.
Build a fixed sleep schedule every day, limit the use of caffeine and stimulants in the evening. Keeping your body moving regularly also helps improve sleep quality every night. Applying these habits is the way to “sleep your way to a smarter brain”. Supports intellectual consolidation through scientific and healthy sleep.
A Simple Guide to Sleep and Brain Health
When to Seek Help
When you experience some signs such as persistent difficulty sleeping, forgetfulness, loss of concentration, or irritability that do not improve, despite trying to adjust your habits and lifestyle. At this point, you need to seek help from a neurologist or sleep therapist. Because disorders that occur in your body, if not treated promptly, can cause serious damage to your brain and mental health. Seeking early intervention from certified sleep coaches can also help prevent cognitive decline and other serious complications from occurring.
Conclusion
Sleep plays a key role in helping to maintain and protect brain health through self-recovery mechanisms, improving memory and regulating emotions. Sleep and brain function are closely linked, impact each other and especially affect learning and work performance and also help prevent neurodegenerative diseases. Prioritizing enough and quality sleep not only helps improve work performance but also protects the brain for long-term health. Therefore, start maintaining the habit of getting enough sleep today, to keep your intelligence and mental health stable and sustainable.