In the digital era, screens are an inseparable part of daily life. From smartphones to laptops and televisions, we spend hours surrounded by artificial light. Yet few realize the impact of blue light on sleep, which can significantly affect overall sleep quality and well-being. Understanding the link between blue light and sleep is the first step to improving your nighttime rest and protecting your natural sleep rhythm.
About Blue Light
It is mandatory to first understand what blue light is and where it comes from before delving into the effects of blue light on sleep systems.
Blue is a fabulous light, a kind of visible light with high energy and shorter wavelengths ranging from 380 to 500 nanometers in wavelength. It is a part of the natural light spectrum that sets the atmosphere that keeps us alert and awake during the day. There is good side to moderate exposure that improves mood and concentration, whereas overexposure at night can hamper the body’s circadian rhythm.
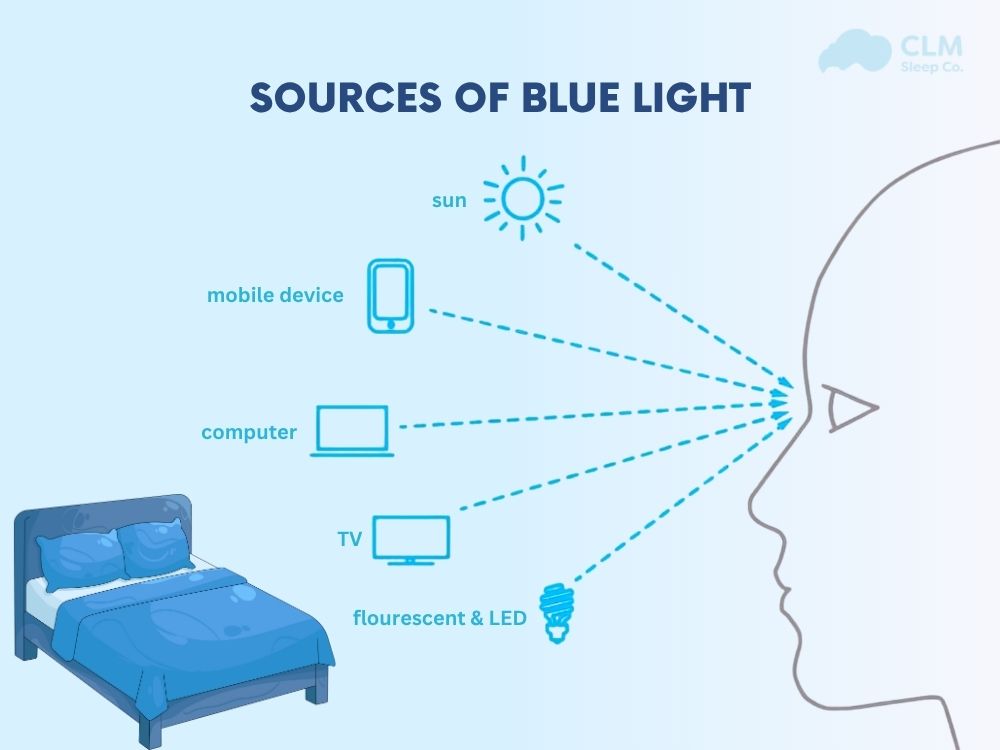
Blue light has both natural and artificial sources. The sun is the chief natural source of blue light regulating our circadian rhythm. Artificial sources of blue light satisfy, to fully extend, wakeful night-time activities. They include:
- Sunlight, which is an essential source of blue light by day
- Digital screens: smartphones, laptops, televisions, etc.
- LED and fluorescent bulbs: home and office varieties
- Electronic gadgets: tablets, smartwatches, digital clocks
While sunlight keeps you awake, any excessive exposure to artificial blue light during the late evening will brainwash your brain to believe that it is still daytime.
How Does Blue Light Affect Sleep?
To realize the effect of blue light on sleep, one has to see how it interacts with melatonin, the hormone controlling the sleep-wake rhythm. Melatonin is responsible for branding a sign to hear the body that it is time to sleep. Usually, in the evening, melatonin levels begin to rise before attaining their highest concentration during the nighttime. However, if blue light radiance comes from the screens, the brain views this light as daylight. Therefor, it delays melatonin secretion and shifts the circadian rhythm, making it very difficult to fall asleep. Some scientific studies also indicate that short-term exposure to blue light can reduce melatonin levels and total sleep hours. (Gooley et al.,2010). If this condition persists, it can lead to a decline in sleep quality, resulting in daytime fatigue and sluggishness.. Consequently, blue light has to be managed so one can exercise good sleep hygiene.
Besides the impact of blue light, it’s also important to understand the stages of sleep. Each night, we cycle through about 4–6 sleep cycles, each lasting 70–110 minutes and including NREM (transition to sleep, light sleep, and deep sleep) and REM sleep. NREM helps the body recover and restore energy, while REM supports learning, memory, and emotional balance. Missing deep sleep can lead to fatigue and poor focus, whereas lack of REM sleep may cause mood swings and reduced concentration. Good sleep depends not only on duration but also on completing full sleep cycles.
Read more: Why do we need sleep, how many hours of sleep do we need, how much deep sleep is normal, how to get more deep sleep, how much rem sleep should you get, how to get more rem sleep
Signs Your Sleep Is Affected by Blue Light
To gain insight into the early symptoms of blue light intervention and successfully treat the scenario before sleep problems turn chronic. A set of commonly observed symptoms in individuals who stay glued to their devices in bed would include:
- Lying there unable to fall asleep while still tired.
- Waking up several times throughout the night.
- Feeling groggy or unrefreshed when receiving a good few hours of sleep.
- Experienced eye strain and headaches often after looking at digital devices.
- Trouble concentrating and having low levels of energy during the day.
These symptoms often suggest that blue light is disturbing your natural sleep pattern and affecting how your body restores itself overnight.
Common Sleep Problems
Exposure to blue light can act as a causative or contributing factor for many sleep-related problems. The knowledge about them gives you the opportunity of protecting your rest much more.
- Insomnia: It is a condition where one has trouble falling asleep or staying asleep with the added cause of suppression of melatonin.
- Circadian rhythm disorders: When the body’s internal clock becomes shifted out of sync with normal day and night behavior.
- Sleep Apnea: There is no direct cause from blue light; rather, disrupted sleep cycles exacerbate symptoms.
- Excessive daytime sleepiness: Daytime fatigue, irritability, and decreased concentration come as a direct consequence of decreased sleep quality.
Improving your light habits is one of the simplest ways to reduce these problems and support better long-term sleep quality.
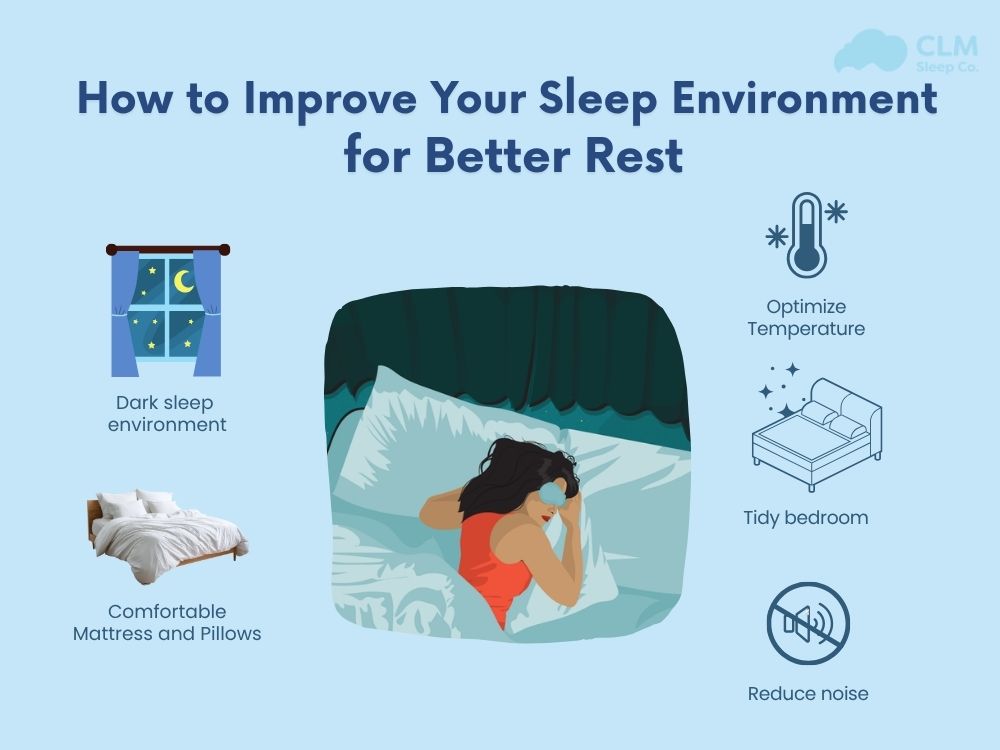
Tips to Reduce the Impact of Blue Light on Sleep
Knowing how to limit blue light exposure is crucial to protect your sleep. One need not completely banish screens but following better habits can make a huge difference.
Limit Screen Use Before Bedtime
Don’t take your phone, computer, or TV anywhere near one to two hours before you sleep. Your brain needs time to wind down naturally, helping melatonin levels increase and making falling asleep easier having that extra resting mind time.
Activate Night Mode
Most devices these days come equipped with blue light reduction settings. For example, iPhones have Night Shift, whereas on Android or Windows, one goes for something called Night Light. You may also want to try third-party utilities such as f.lux or Twilight, which complement the system ones. These filters tint the screens to warmer shades, cutting glare and strain.
Adjust Bedroom Lighting
Opt for warm light bulbs under 3,000K to make a soft and soothing ambiance for sleep. Turn off or cover LED indicator lights, such as those from TVs, digital clocks, or other artificial light sources. This soft lighting cues your body to start relaxing.
Use Blue Light Blocking Glasses
If blue light sources must be used in the evening, wear blue light blocking glasses, which filter the harmful wavelengths that otherwise would have disrupted melatonin production, allow
Get Natural Daylight Exposure
Spending time outdoors, especially in the morning, helps regulate your circadian rhythm. Just 20 to 30 minutes of sunlight early in the day can improve mood, alertness, and nighttime sleep quality.
Maintain a Regular Sleep Routine
A consistent sleep schedule is one of the best ways to strengthen your internal clock. Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, even on weekends. This regularity helps your body naturally prepare for sleep at night.
Read more: How to Build a Healthy Bedtime Routine for Better Sleep
Replace Screen Time with Relaxing Habits
Instead of scrolling through your phone before bed, try more relaxing alternatives. You can read a physical book, listen to calm music, meditate, or practice deep breathing. These activities encourage relaxation and signal your mind to slow down before sleep.
FAQs
Many people have questions about how blue light influences sleep. Below are some of the most common concerns answered by sleep experts.
Do Blue Lights Affect Your Sleep?
Yes. Blue light directly affects sleep by delaying melatonin release and confusing your brain’s perception of night and day. Consistent exposure at night can make it harder to fall asleep and reduce sleep quality.
How Long Should I Avoid Blue Light Before Bed?
Sleep specialists recommend avoiding blue light exposure for at least one to two hours before bedtime. If you cannot, reduce brightness levels, activate night mode, or wear blue light glasses to minimize the impact.
What Is the Best Light Color for Sleep?
Warm colors such as red, orange, or amber are best for promoting sleep. These tones have longer wavelengths that do not interfere with melatonin and help your body relax naturally.
How Blue Light Affects Sleep
Blue light impacts sleep by suppressing melatonin and shifting your internal clock later into the night. Over time, this can lead to insomnia, fatigue, and decreased cognitive performance. Reducing screen time in the evening is one of the simplest ways to restore balance.
Conclusion
In our technology-driven world, blue light exposure has become an unavoidable part of life. However, by understanding how blue light on sleep affects your body and applying simple lifestyle adjustments, you can protect your rest and wake up feeling refreshed.
At CLM Sleep, we believe that healthy sleep starts with awareness and mindful choices. Limit evening screen use, embrace natural daylight, and create a relaxing nighttime routine. Your body will thank you with deeper, more restorative sleep and brighter mornings. Contact CLM Sleep today for FREE sleep consultation if you are experiencing sleep issues.