According to the Better Health Channel, a health resource managed by the Victorian Government, “It’s estimated that about 5% of Australians have sleep apnoea, with around 1 in 4 men over the age of 30 affected. In the over-30 age group, the disorder is about 3 times more common in men than women.” With common symptoms such as snoring, frequent nighttime awakenings, and excessive daytime sleepiness, diagnosing sleep apnea is essential. Early treatment not only improves your quality of life but also helps you avoid serious conditions such as cardiovascular disease and stroke. This article of CLM Sleep explores the sleep apnea diagnosis process, testing methods, and associated health risks to help you take charge of your sleep health.
Read more: Can You Have Sleep Apnea Without Snoring?
What is sleep apnea diagnosis?
Sleep apnea diagnosis is the process of identifying people who have sleep apnea. At the same time, it helps determine the cause, type of sleep apnea, and severity of the condition. Sleep apnea occurs during sleep, making it often very difficult to detect. Beside symptoms that occur during sleep, such as snoring, pauses in breathing, or choking sounds, patients can also rely on daytime symptoms like feeling tired even after getting enough sleep, excessive daytime sleepiness, or difficulty concentrating at work and in daily activities.
See more: Can You Have Sleep Apnea Without Snoring?
The process of diagnosing sleep apnea typically involves multiple steps, including clinical examination, symptom assessment, and the performance of tests as directed by the doctor. But basically, you’ll know if you have sleep apnea and its current severity thru the AHI (Apnoea–Hypopnoea Index). If your AHI is greater than 15, you are considered to have sleep apnea. The higher this index, the more severe the disease.
Why diagnosis matters
Detecting and treating sleep apnea can help you improve your sleep quality as well as your quality of life, significantly reducing daytime fatigue, sleepiness, and lack of focus. Not only that, but early treatment also helps you decrease the risk of serious health conditions such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and stroke. Although sleep apnea is common and has a significant impact, many cases remain undiagnosed. Therefore, raising awareness about sleep health, recognizing sleep apnea symptoms, and ensuring early diagnosis are essential. Not only does it improve public health, but it also reduces the risk of serious diseases and the burden of costly treatment
See more: The phenomenon of tachypnea after an apnea episode
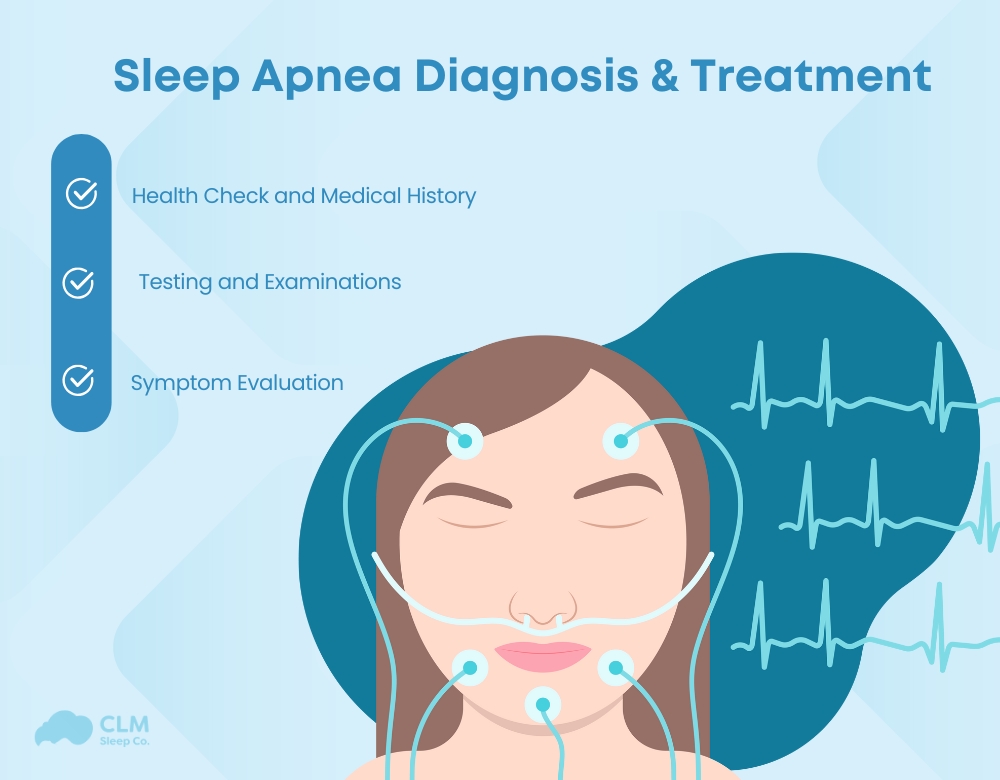
Diagnosis Process of Sleep Apnea
Proper diagnosis of sleep apnea involves a step-by-step process to evaluate symptoms, medical history, and physical characteristics. This ensures an accurate understanding of the condition’s presence and severity.
Health Check and Medical History
Clinical Examination
Doctors begin by assessing physical factors that may contribute to sleep apnea. These include the size and structure of the airway, neck circumference, and body mass index (BMI). For example, individuals with a thick neck or a narrow airway are at higher risk of developing obstructive sleep apnea.
Personal and Family Medical History
Understanding a patient’s medical history is essential. This involves gathering details about sleep patterns, chronic illnesses like hypertension or diabetes, and any family history of sleep disorders. A predisposition to conditions such as snoring or apnea in close relatives may suggest an inherited risk.
Symptom Evaluation
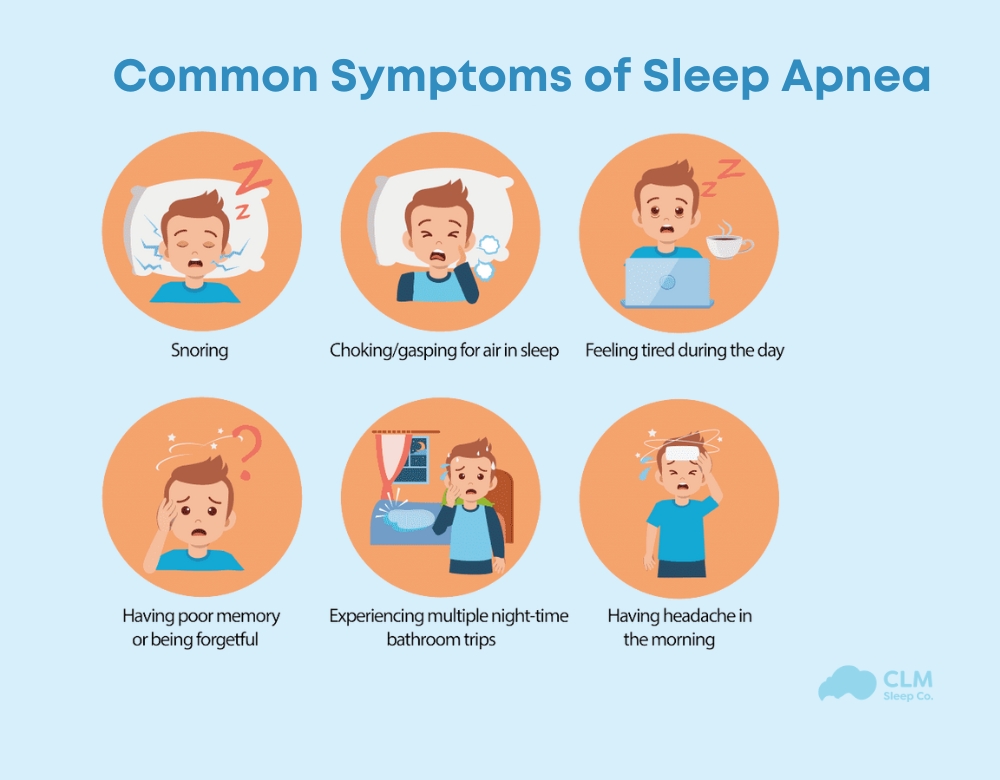
Common Symptoms
Patients are asked about noticeable symptoms that are typical of sleep apnea, such as:
- Loud snoring, often reported by a partner
- Episodes of gasping or choking during sleep
- Morning headaches that occur frequently
- Excessive daytime sleepiness, even after a full night of rest
Risk Level Assessment
Based on the frequency and severity of these symptoms, sleep apnea is classified into three levels:
- Mild: Symptoms occur sporadically and have minimal impact on daily activities.
- Moderate: Symptoms are more frequent and begin to affect quality of life.
- Severe: Symptoms are persistent and significantly impair daily functioning.
Testing and Examinations
To confirm a sleep apnea diagnosis, doctors utilize a variety of diagnostic tests:
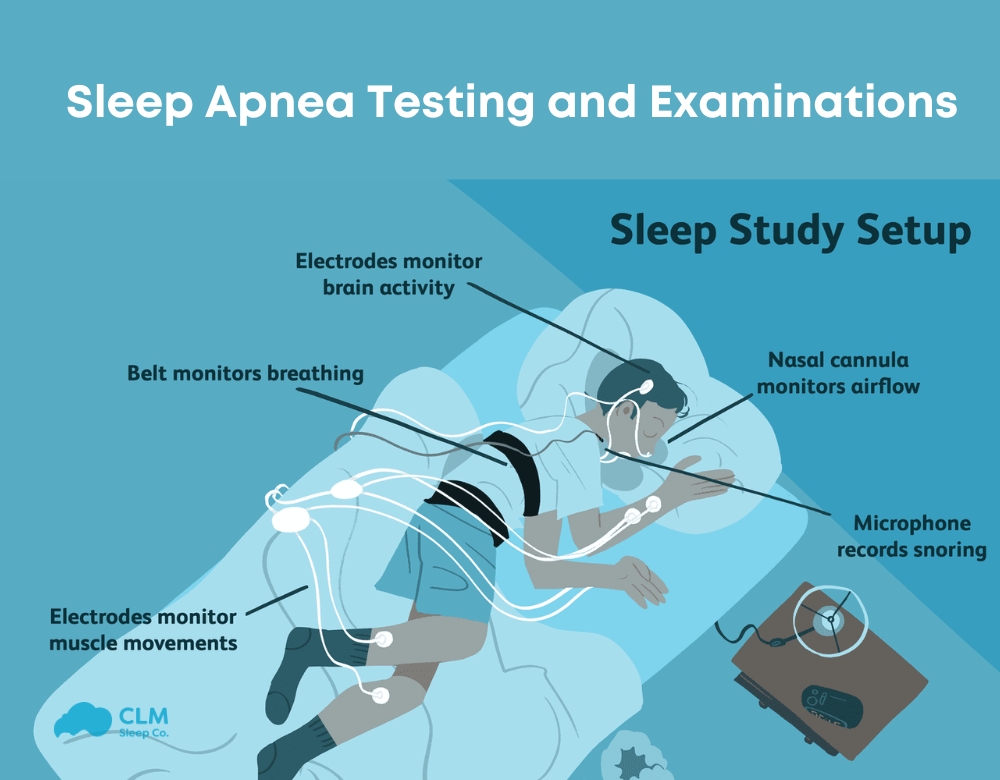
- Polysomnography (PSG): A comprehensive in-lab sleep study that measures brain activity, heart rate, and breathing patterns.
- Home Sleep Tests (HSAT): Portable monitoring devices that assess breathing and oxygen levels during sleep.
- Oximetry: A simple, non-invasive test that tracks oxygen saturation overnight.
- Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT): Used to evaluate excessive daytime sleepiness and narcolepsy-related conditions.
Methods of Testing to Diagnose Sleep Apnea
Several diagnostic methods are used to confirm sleep apnea, each tailored to assess specific symptoms and severity levels. These methods help doctors determine the most suitable treatment options.
Home Sleep Studies (HSAT)
Home Sleep Studies are designed to monitor sleep patterns in a familiar environment. They focus on identifying breathing irregularities, oxygen level drops, and heart rate changes during sleep.
These tests measure key indicators such as apnea episodes (instances of interrupted breathing) and oxygen saturation (the amount of oxygen in the blood). HSAT is particularly suitable for patients with mild to moderate sleep apnea, providing a convenient and cost-effective alternative to laboratory-based studies.

Laboratory Sleep Studies (PSG)
Polysomnography (PSG) is the gold standard for diagnosing sleep disorders. Conducted in a sleep clinic or laboratory, it provides detailed and accurate data on various physiological parameters during sleep. It measures brain activity (EEG), eye movements (EOG), oxygen levels in the blood, heart rate (ECG), and muscle activity (EMG).
PSG is suitable for diagnosing all levels of sleep apnea, particularly severe cases, and is often recommended when other diagnostic tests yield inconclusive results.

MSLT
The Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT) evaluates how quickly a person falls asleep during the day, making it a valuable tool for assessing excessive daytime sleepiness and diagnosing conditions like narcolepsy. It measures sleep onset time, indicating how rapidly an individual transitions from wakefulness to sleep. This test is particularly suitable for patients with severe sleep apnea who experience pronounced fatigue and persistent drowsiness during the day.
Driving Simulator
A driving simulator assesses the impact of sleep apnea on cognitive functions crucial for safe driving, such as reaction times and mental alertness. This method is particularly suited for individuals with severe sleep apnea who experience cognitive impairments or issues with daytime performance.
Oximetry
Oximetry is a straightforward method used to measure oxygen saturation levels overnight, identifying breathing irregularities linked to sleep apnea. It tracks oxygen desaturation events, indicating drops in oxygen levels during sleep. This test is particularly suitable for individuals with mild sleep apnea or as an initial screening tool before proceeding to more comprehensive diagnostic evaluations.
Risks of Sleep Apnea to Health
Sleep apnea, if left untreated, poses serious risks to overall health and well-being. Below are the major health complications associated with this condition:
Cardiovascular Problems
Sleep apnea significantly increases the risk of high blood pressure (hypertension) and heart disease. Repeated interruptions in breathing cause oxygen levels to drop, triggering stress responses that strain the cardiovascular system. This can lead to arrhythmias, heart attacks, and even strokes.
Metabolic Issues
Sleep apnea is closely linked to metabolic disorders, including type 2 diabetes and obesity. The condition disrupts glucose metabolism and increases insulin resistance, contributing to the development and progression of diabetes. Additionally, poor sleep quality often leads to weight gain, creating a vicious cycle of worsening apnea symptoms.
Cognitive Impairment
The repeated interruptions in sleep cycles impair memory and reduce mental alertness. Sleep apnea can cause difficulty concentrating, slower reaction times, and long-term cognitive decline, including an increased risk of dementia.
Respiratory Issues
For individuals with pre-existing lung conditions, sleep apnea exacerbates respiratory failure and increases complications. Chronic oxygen deprivation during sleep can worsen diseases like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma.
Increased Risk of Accidents
Daytime sleepiness caused by sleep apnea significantly raises the likelihood of accidents at work or while driving. Reduced alertness and slower reaction times make individuals more prone to mishaps, endangering both themselves and others.
Reduced Quality of Life
Poor sleep quality leads to chronic fatigue, irritability, and difficulty performing daily activities. Over time, this affects emotional well-being, relationships, and productivity, diminishing overall life satisfaction.
Sexual Dysfunction
Sleep apnea can lower libido and cause sexual dysfunction in both men and women. This is often linked to hormonal imbalances and the overall physical strain caused by poor-quality sleep.
Addressing these risks through early diagnosis and treatment is crucial to preventing long-term health consequences and improving quality of life.

Conclusion of the article
Sleep apnea diagnosis is a critical step in addressing a condition that significantly impacts overall health and quality of life. Through proper evaluation, including symptom assessment, medical history review, and diagnostic tests, individuals can receive tailored treatment to manage their condition effectively. Whether it’s a sleep apnea diagnosis at home with convenient tools like HSAT or a comprehensive in-lab study, accurate diagnosis is key to preventing complications such as heart disease, diabetes, and cognitive impairment.
If you’re seeking reliable services for sleep apnea diagnosis near me or exploring options for sleep apnea diagnosis in Adelaide, professional care is just a step away. Visit CLM Sleep Services to learn more about diagnostic solutions or explore CPAP Discount for treatment options that suit your needs. Take control of your sleep health today and experience the benefits of restful, rejuvenating sleep.
Reference
- Neuroscience Research Australia (NeuRA). (n.d.). Sleep apnoea. In Translational Neuroscience.
- Better Health Channel. (n.d.). Sleep apnoea.