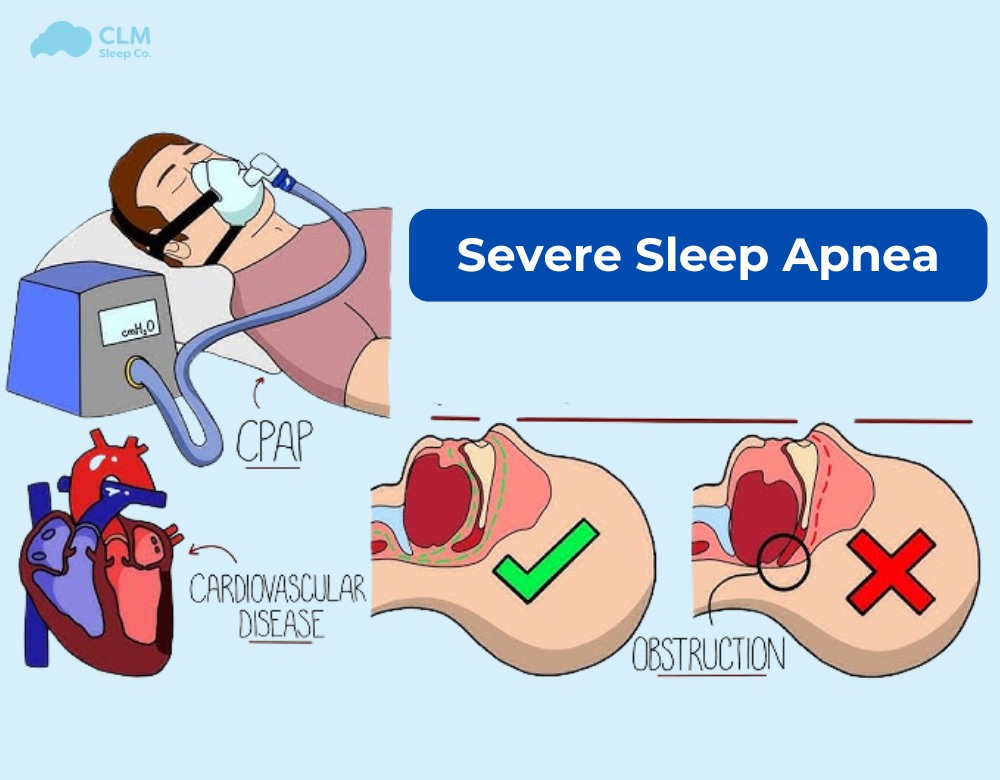
Severe sleep apnea, often with an AHI > 30, is a dangerous sleep disorder that increases the risk of stroke by 2.86 times in men and 1.8 times in women, as well as increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases by up to 1.68 times compared to individuals with a normal AHI of less than 5. People with severe sleep apnea often exhibit very clear symptoms such as loud snoring while sleeping; gasping, chest pain, or tightness while sleeping; and frequently waking up startled in the middle of the night. These individuals must have a specific treatment plan and strictly follow the doctor’s instructions. In this article, CLM Sleep will help you better understand severe sleep apnea and how to detect sleep apnea early.
What is Severe Sleep Apnea?
Severe sleep apnea is considered the extreme form of sleep apnea, which describes a condition in which an individual’s airway becomes blocked repeatedly during sleep. In severe cases, the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI), which tallies the number of apneas (breathing pauses) and hypopneas (shallow breathing) observed per hour, typically exceeds 30, meaning that an affected person will have at least 30 stoppages in breathing per hour of sleep.
The severity of sleep apnea is determined by the AHI according to the table below:
| Sleep apnea severity | AHI score | Breathing disruptions per hour |
| Mild sleep apnea | 5–15 | 5–15 |
| Moderate sleep apnea | 15-30 | 15-30 |
| Severe sleep apnea | Over 30 | Over 30 |
There are three severe types of sleep apnea, and they all have distinctly different causes and characteristics:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea: By far the most common form of sleep apnea, OSA results from over-relaxation of muscles at the back of the throat, causing the airway to become partially or even fully obstructed. In a severe case, the patient’s airway may become blocked thirty or more times an hour, disrupting sleep and the body’s supply of oxygen.
- Central Sleep Apnea: Unlike obstructive sleep apnea, in central sleep apnea, the brain fails to transmit the signals to the muscles that are responsible for controlling breathing— as a result, no physical blockage, and yet the patient suffers from intermittent cessations in breathing. Less prevalent than OSA, this form can also prove itself to be quite severe.
- Complex Sleep Apnea: This is otherwise called treatment-emergent central sleep apnea. It combines both obstructive and central sleep apnea. It may look like an episode of obstructive sleep apnea, but it turns into a mixed form of apnea at the time of treatment, often with CPAP.
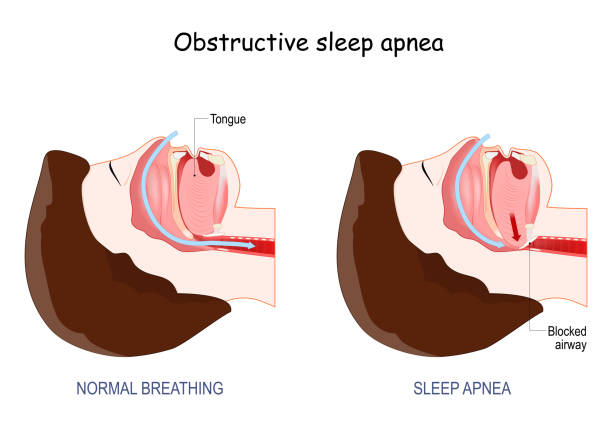
Symptoms of Severe Sleep Apnea
There are 3 common levels of sleep apnea: mild sleep apnea, moderate sleep apnea, and severe sleep apnea. Severe Sleep Apnea is the most severe level, causing serious sleep disturbances and affecting overall health. The symptoms of Severe Sleep Apnea are very clear, and you must have noticed them for a long time. Here are the common symptoms of this condition:
Nighttime Symptoms
- Very loud snoring, frequently interrupted by long pauses in breathing.
- Multiple awakenings at night, sometimes accompanied by choking or gasping.
- Severe breathing interruptions that disturb sleep cycles.
- Waking up with feelings of panic or choking.
- Frequent need to urinate during the night (nocturia).
- Chest pain or tightness during sleep.
Read more: The phenomenon of tachypnea after an apnea episode
Daytime Symptoms
- Extreme fatigue and excessive daytime sleepiness, significantly impairing daily life.
- Irritability, memory problems, and difficulty concentrating.
- High risk of accidents due to lack of alertness.
- Uncontrollable daytime sleepiness (microsleeps), often dozing off during tasks like driving or working.
- Voice changes (possibly due to vocal cord irritation linked to breathing issues).
- Reduced libido or sexual dysfunction (e.g., erectile dysfunction in men).
- Signs of severe depression or anxiety.
Additional Symptoms Common Across All Levels
- Difficulty managing weight (often prone to weight gain due to metabolic changes).
- Dry mouth or bad breath in the morning.
- Digestive issues, such as acid reflux or heartburn, possibly linked to nighttime episodes.
See more: Top Obstructive Sleep Apnea Symptoms
Risk Factors
You develop a higher chance of suffering from severe sleep apnea if:
Overweight or obese
The most important risk factor by far is the presence of obesity, more than 20% of affected individuals have OSA compared to around 3% of people of average weight. Being overweight increases fat accumulation around the neck and throat, leading to narrowing of the upper airway and obstruction during sleep.
Male gender
A man is two to three times more likely than a premenopausal woman to have sleep apnea. This is because men tend to have narrower airways, more soft tissue, and less estrogen protection, which makes the airway weaker and more prone to collapse. After menopause, the risks are about equal for males and females.
Family history
The risk could be higher if one of your family members has sleep apnea too. Genetic factors can affect jaw structure, neck circumference, and muscle tone—for example, a small or recessed lower jaw, weak throat muscle tone, or a large neck circumference. These inherited traits can significantly increase the likelihood of airway obstruction during sleep.
Age
As you get older, muscle tone in the throat tends to decrease, which can make the airway more likely to collapse. The risk increases with age, especially in your 60s and 70s.
Smoking
Heavy smoking causes chronic inflammation and swelling of the throat and nasal lining, which narrows the upper airway and increases airflow resistance. Therefore, smokers are more likely to have sleep apnea.
Coexisting health conditions
People who also have high blood pressure, diabetes, or asthma often experience metabolic disturbances and hormonal imbalances that can affect breathing during sleep. These conditions may raise the risk of developing sleep apnea.
Chronic nasal congestion
People with chronic nasal congestion are twice as likely to develop sleep apnea compared to those without it. This condition makes it difficult to breathe through the nose, forcing individuals to breathe through their mouth during sleep. Mouth breathing increases the risk of throat and upper airway narrowing, especially during deep sleep when muscle tone naturally decreases. This significantly raises the likelihood of experiencing obstructive sleep apnea.
Narrowed airways
Issues that narrow the airways, such as enlarged tonsils or adenoids, also can also raise the risk of sleep apnea. This is because a narrowed airway reduces the breathing space, causing mechanical obstruction of the upper respiratory tract, especially when lying down.
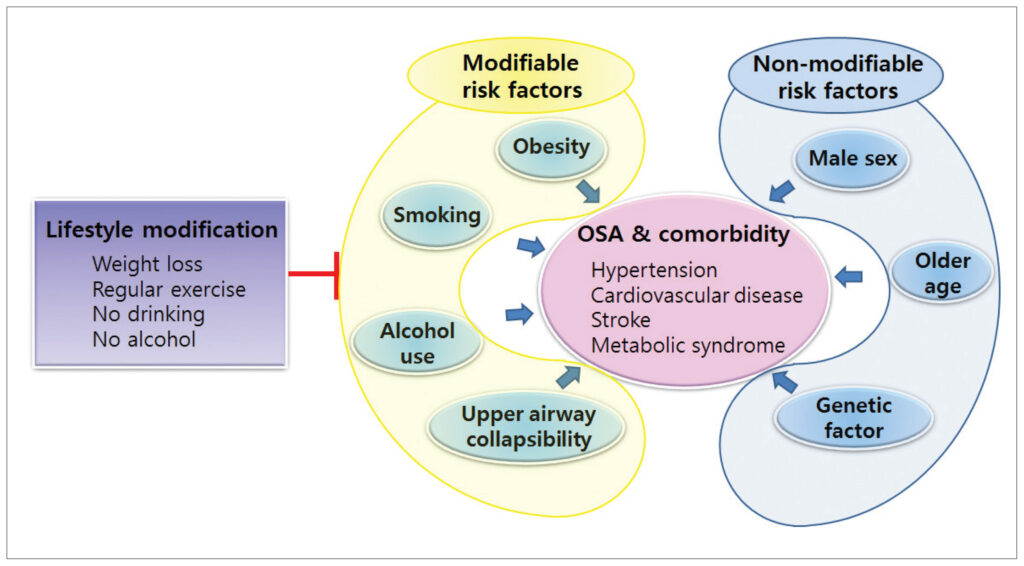
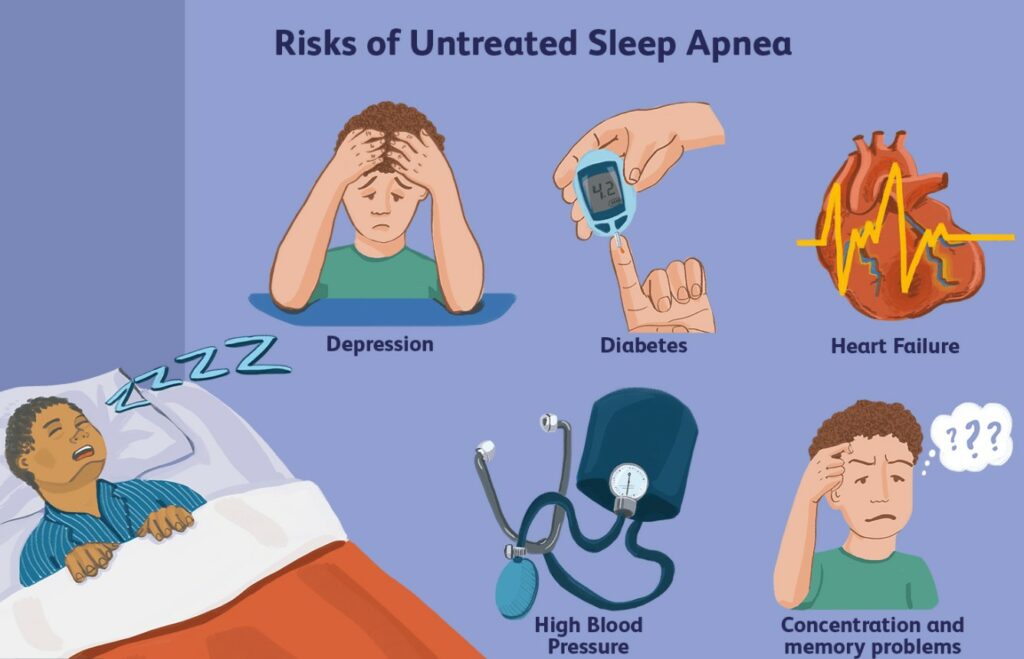
Health Risks
According to the American Sleep Apnea Association (ASAA), undiagnosed and untreated sleep apnea can lead to several serious health impacts, including:
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Stroke
- Depression
- Diabetes
Sleep apnea can also result in indirect consequences, such as an increased risk of traffic accidents due to drowsiness while driving.
See more: Can Sleep Apnea Kill You? Risks and Consequences
Diagnosis of Severe Sleep Apnea
Diagnosis of severe sleep apnea requires a sleep study, during which you will be monitored while sleeping. This process can occur in a specialized facility (in-lab sleep study) or at home (home sleep study).
The doctor will also examine your throat, neck, and mouth, as well as ask about your medical history and sleep symptoms. If you have severe sleep apnea, you may need a blood test to rule out other conditions, such as hypothyroidism.
See more: Guide to Sleep Apnea Test At Home Quick and Easy
Severe Sleep Apnea Treatment
Sleep apnea can cause many health complications if left untreated. However, several effective treatment methods are available, tailored to each patient’s needs and severity of the condition. For severe sleep apnea, here are some common treatment options.
Lifestyle changes
A number of measures will be recommended to individuals with severe sleep apnea to improve their health:
- Keeping a healthy weight is important
- Smoking should be stopped
- Regular exercise is essential
- Consume less alcohol
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
One of the most common treatments for severe sleep apnea is a CPAP machine. This device provides a continuous airflow through a mask, helping to keep the airway open throughout sleep. CPAP machines effectively reduce the frequency of apneas and improve sleep quality. However, adjustments may be needed to find each user’s best mask type and pressure settings.
Bi-level Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP)
Bi-level Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) is a non-invasive ventilation therapy commonly used to treat severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). BiPAP is particularly useful for patients who do not find comfort with CPAP machines.
The BiPAP machine delivers two levels of air pressure:
- Higher Inhalation Pressure (IPAP): This assists inhalation and keeps the airway open.
- Lower Exhalation Pressure (EPAP): This makes exhalation easier.
Surgery
Doctors may recommend several surgical options, including:
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) to remove excess tissue and create space for the airway.
- Upper airway stimulation to improve airflow.
- Jaw surgery to create additional space for the airway.
- Tracheostomy is typically performed in severe, life-threatening cases of obstructive sleep apnea.
- Implantation of devices to reduce upper airway collapse.
Oral appliances
Dental devices are designed to reposition the jaw and tongue, helping to keep the airway clear. These devices are very useful for individuals with mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnea and may also benefit some severe sleep apnea cases. They are often considered more comfortable than CPAP machines and are easier to travel with and use. However, to ensure effectiveness, it’s important to consult a dentist or orthodontist specializing in sleep apnea.
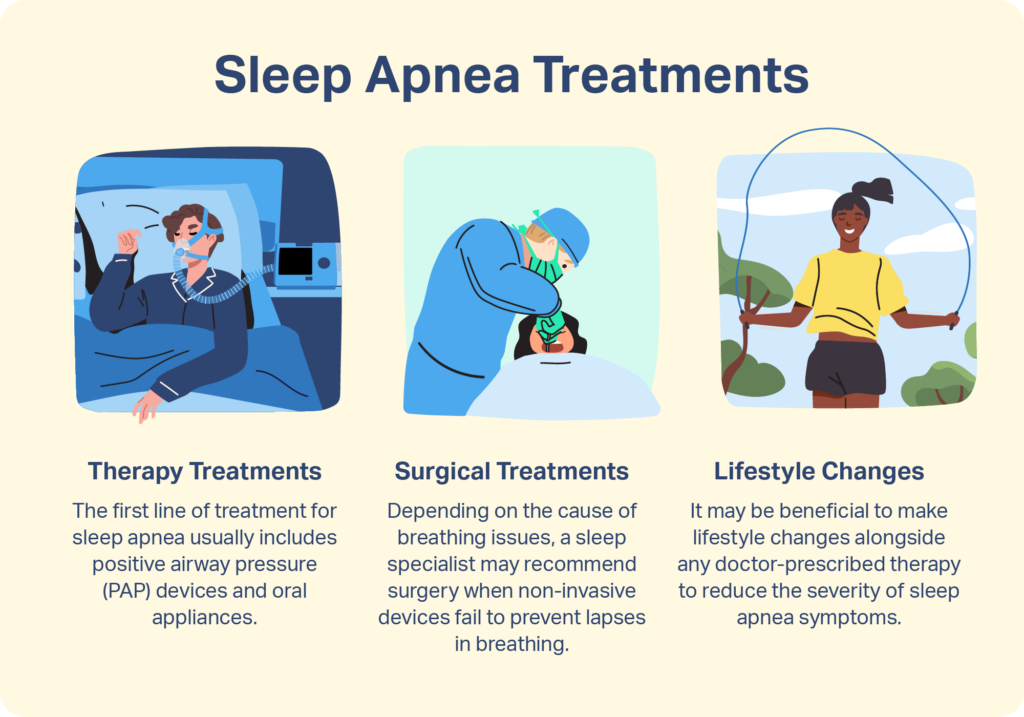
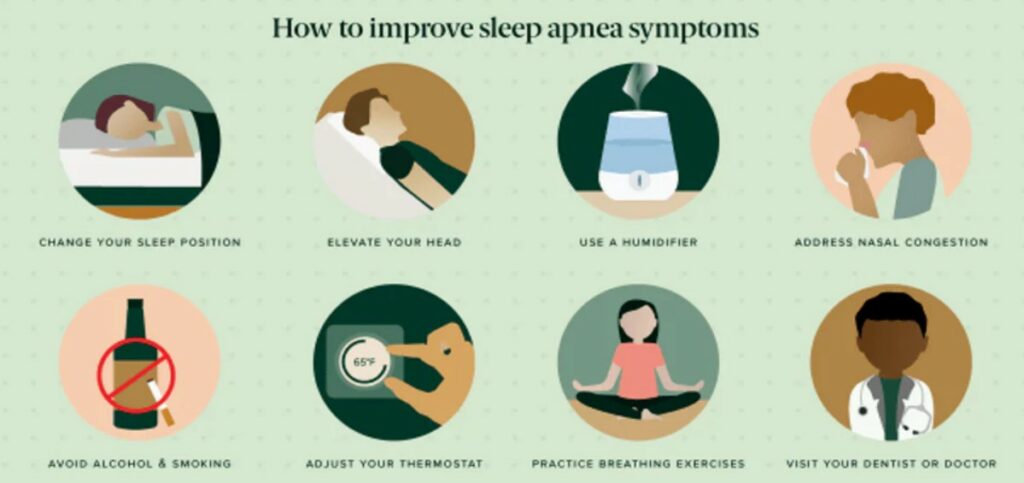
Prevention
You must make lifestyle changes and adopt proactive measures to prevent severe sleep apnea. Here are some effective strategies:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a major risk factor for severe sleep apnea. Losing weight can help improve or eliminate symptoms for many individuals.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and enhances overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week.
- Avoid Alcohol and Sedatives: Alcohol and sedatives can relax the muscles in the throat, worsening sleep apnea. It’s best to avoid these substances, especially before bedtime.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking increases inflammation and fluid retention in the upper airway, leading to sleep apnea. Quitting smoking not only improves overall health but also reduces the severity of symptoms.
- Sleep on Your Side: Sleeping on your back can exacerbate sleep apnea. Try to sleep on your side to keep the airway open.
- Establish a Regular Sleep Routine: Going to bed and waking up simultaneously daily will improve sleep quality and regulate your body’s internal clock.
- Avoid Heavy Meals Before Bed: Eating large meals close to bedtime can increase the likelihood of sleep apnea. Aim to have dinner at least two to three hours before sleeping.
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can thicken mucus in the throat, leading to airway obstruction. Ensure you drink enough water throughout the day.
- Manage Allergies and Nasal Congestion: Allergies and nasal congestion can worsen sleep apnea. Use decongestants or antihistamines as needed and keep your sleeping environment allergen-free.
- Regular Medical Checkups: Regular visits to your healthcare provider help monitor your health and catch any potential issues early, allowing for timely intervention.
Conclusion of the article
Severe sleep apnea is a sleep disorder that can have serious health consequences if left untreated. Early recognition of symptoms and seeking medical evaluation are crucial. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, CPAP therapy, BiPAP therapy, oral appliances, and surgery, all of which help reduce sleep apnea symptoms and improve quality of life. Understanding the risk factors and implementing preventive measures is the best way to minimize the risk of this condition. If you suspect you or a loved one may be affected, consult a specialist for diagnosis and personalized treatment planning.
Visit our website to explore more about managing sleep disorders and their impact on health. Discover additional resources from experts to help you achieve better sleep at night. At the same time, choose high-quality sleep apnea treatment devices that are suitable for each individual and come from well-known brands such as ResMed, F&P, Phillips, etc. Check out CPAP Adelaide and and shop our CPAP Discount Warehouse online store.
Reference
1. Jennifer M. Slowik; Abdulghani Sankari; Jacob F. Collen. Obstructive Sleep Apnea. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2025 Mar.
2. Alkatib, S., Sankri-Tarbichi, A. G., & Badr, M. S. The impact of obesity on cardiac dysfunction in patients with sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep and Breathing. 2014;18(1):137-142. DOI: 10.1007/s11325-013-0861-0. PMID: 23673872
3. Saeed, S., Romarheim, A., Solheim, E., Bjorvatn, B., & Lehmann, S. Cardiovascular remodeling in obstructive sleep apnea: Focus on arterial stiffness, left ventricular geometry and atrial fibrillation. Expert Review of Cardiovascular Therapy. 2022;20(6):455-464. DOI:10.1080/14779072.2022.2081547. PMID: 35673889
4. Tadic, M., Gherbesi, E., Faggiano, A., Sala, C., Carugo, S., & Cuspidi, C. The impact of continuous positive airway pressure on cardiac mechanics: Findings from a meta-analysis of echocardiographic studies. Journal of Clinical Hypertension (Greenwich, Conn.). 2022;24(7):795-803. DOI:10.1111/jch.14488.PMID: 35695237. PMCID: PMC9278581
5. Zhang X, et al. Association between obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome and the risk of cardiovascular diseases: an updated systematic review and dose‑response meta‑analysis. Sleep Med. 2020 Jul;71:39–46. DOI :10.1016/j.sleep.2020.03.011. PMID: 32485597
6. Redline S, Yenokyan G, Gottlieb DJ, Shahar E, O’Connor GT, Resnick HE, et al. Obstructive Sleep Apnea–Hypopnea and Incident Stroke. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010 Mar 25;182(2):269–277. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200911-1746OC. PMCID: PMC2913239 PMID: 20339144
7. Jean-Louis G, Zizi F, Clark LT, Brown CD, McFarlane SI. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Disease: Role of the Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components. J Clin Sleep Med. 2008 Jun 15;4(3):261–272. PMCID: PMC2546461 PMID: 18595441
8. Rivas M, Ratra A, Nugent K. Obstructive sleep apnea and its effects on cardiovascular diseases: a narrative review. Anatol J Cardiol. 2016 Nov;15(11):944–950. doi: 10.5152/AnatolJCardiol.2015.6607. PMCID: PMC5336948 PMID: 26574763
9. Sandeep P. Khot, MD. Sleep and Stroke. Stroke. 2019 Jun;50(6):1612–1617. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023553. PMID: 31043150.
10. Daniel J. Gottlieb, MD, MPH, Gayane Yenokyan, MD, PhD, et al. Prospective Study of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Incident Coronary Heart Disease and Heart Failure: The Sleep Heart Health Study. Circulation. 2010 Jul 27;122(4):352–7. Doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.901801.