Deep sleep is a vital stage of rest that promotes physical healing, memory consolidation, and emotional balance. Without enough deep sleep, your health and daily performance can suffer. at CLM Sleep, We help you understand, improve, and develop restorative deep sleep through expert guidance, testing, and tailored treatment plans. Let’s find out how better can change your life.
What is Deep Sleep?
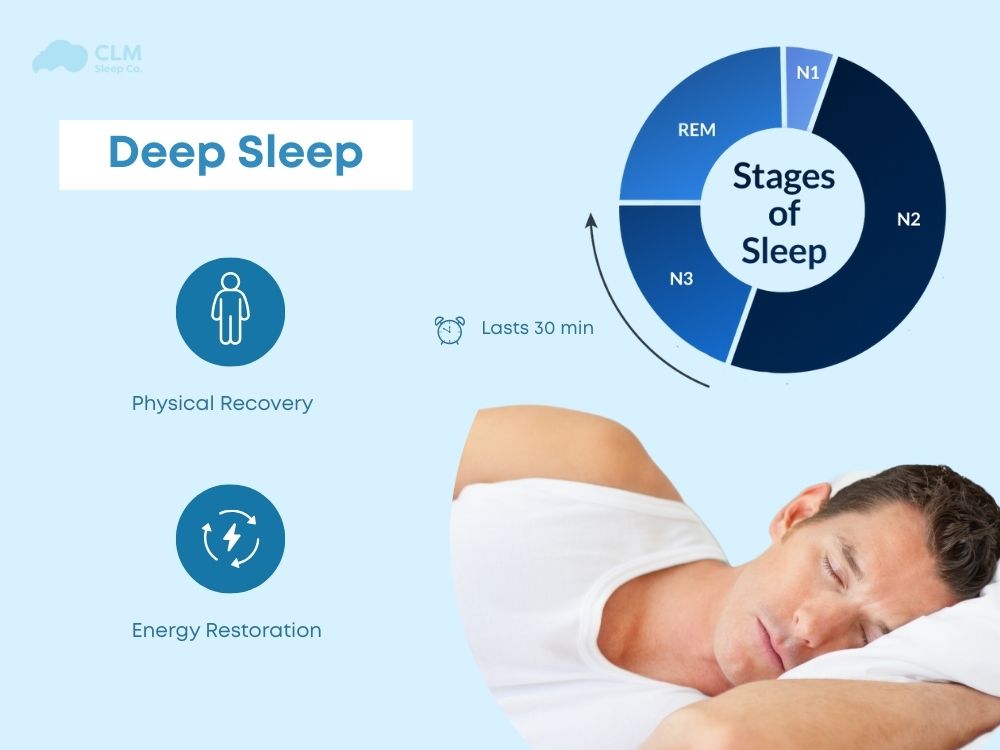
Deep sleep, or slow-wave sleep (SWS), is the third phase and the most restorative stage of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. Slow, high-amplitude delta waves with a frequency of 0.5 to 2 Hertz are generated by the brain during this phase. This stage requires delta waves to be produced for at least 6 seconds within a 30-second window.
Deep sleep generally starts within the first hour of falling asleep and occurs mostly in the early part of the night. During the latter part of the night, deep sleep periods shorten, while the periods of REM sleep are extended.
It generally begins within the first hour of falling asleep and occurs mostly in the early part of the night. During the latter part of the night, these periods shorten, while the duration of REM sleep increases.
Heart rate and respiration slow down during this stage of sleep; your muscles are fully relaxed, and brain activity falls to its lowest point. Restoration of the body takes place in this phase-the repair of injured tissues, regeneration of cells, and so on.
Since brain and body activity is at its lowest levels in this state, it is usually hard to wake someone up during deep sleep. Also, suddenly being awakened at this stage will make one feel groggy, disoriented, or mentally numb-well known as sleep inertia-which could last for 1 hour.
See more: What is Circadian Rhythm Disorder?
Sleep Cycle Stages
There are two major phases of stages of sleep are sleep-a Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep and a Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep phase. Each complete sleep cycle lasts about 90 to 110 minutes and can repeat several times during the night. Deep sleep occurs during stage 3 of NREM sleep in these cycles, which is the most physically relaxing stage.
Overview of NREM and REM Sleep
Here is a comparison chart of sleep stages, outlining their characteristics, durations, and benefits:
| Sleep Stage | Characteristics | Duration (per cycle) | Key Benefits |
| NREM Stage 1 | Light sleep, easy to wake, muscle activity slows | 1-7 minutes | Transition from wakefulness to sleep |
| NREM Stage 2 | Body temp drops, heart rate slows, sleep spindles appear | 10-25 minutes | Memory processing, body relaxation |
| NREM Stage 3 (Deep) | Slow brain waves, hard to wake, most restorative | 20-40 minutes | Physical repair, immune boost, memory consolidation |
| REM Sleep | Dreaming occurs, brain activity increases, body paralyzed | 10-60 minutes | Emotional regulation, learning, brain detoxification |
Why Deep Sleep Mostly Occurs in the Early Part of the Night
Deep sleep tends to occur more in the first half of the night. This is because of how your body follows a natural circadian rhythm – a 24-hour internal clock that regulates your sleep-wake cycle.
In the early stages of the night, the body prioritizes NREM sleep, particularly stage 3 deep sleep, for physical restoration. As the night progresses, REM sleep becomes more dominant, helping support emotional processing and memory.
That’s why going to bed earlier – in alignment with your body’s natural clock – can help you get more high-quality deep sleep and wake up feeling more refreshed.
Benefits of Deep Sleep
Deep sleep offers a wide range of health benefits that support your body, brain, and emotional well-being. Here’s why this stage of sleep is so essential:
- Physical Restoration & Recovery: During this time, your body repairs tissues, builds muscle, and releases growth hormone – all of which promote overall healing and recovery.
- Immune System Boost & Support: Deep sleep strengthens your immune system by promoting the production of infection-fighting cytokines and reducing inflammation.
- Memory Enhancement & Consolidation: This sleep stage helps process and store new information, improving learning ability, long-term memory, and mental focus.
- Emotional Balance & Mood Stability: This stage helps regulate stress hormones and supports better emotional control, reducing anxiety and depression.
- Heart Health & Blood Sugar Regulation: Deep sleep allows your heart rate and blood pressure to drop, while also helping stabilize blood sugar and insulin sensitivity.
- Brain Detoxification: The glymphatic system becomes active during deep sleep, clearing waste and toxins from the brain, including those linked to cognitive decline.
- Increased Energy & Daily Alertness: After a night of restorative sleep, you wake up feeling refreshed, with more energy, sharper thinking, and better overall performance throughout the day.
Signs You’re Not Getting Enough Deep Sleep
Not getting enough deep sleep can impact nearly every aspect of your health and daily life. The table below highlights common warning signs to look out for:
| Sign | Impact |
| Persistent Fatigue | Feeling tired even after a full night’s sleep; struggling to stay energized. |
| Poor Memory & Focus | Difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, or slower thinking. |
| Mood Swings & Irritability | Increased anxiety, depression, or emotional sensitivity. |
| Frequent Illness | Lowered immunity, frequent colds, or slower recovery from sickness. |
| Muscle Aches & Slow Recovery | Soreness that lingers; slow healing after physical activity or injury. |
| Increased Cravings & Weight Gain | Hormonal imbalances leading to sugar cravings or unintentional weight gain. |
| High Blood Pressure | Elevated blood pressure due to reduced cardiovascular recovery at night. |
| Morning Grogginess | Feeling “foggy” or disoriented upon waking; hard to feel fully alert. |
Causes of Reduced Deep Sleep
Several factors can interfere with the body’s ability to enter and maintain deep sleep, including:
- Chronic stress and anxiety
- Irregular sleep schedules (frequent late nights or shift work)
- Caffeine or alcohol consumption too close to bedtime
- Sleep disorders like sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome, or insomnia
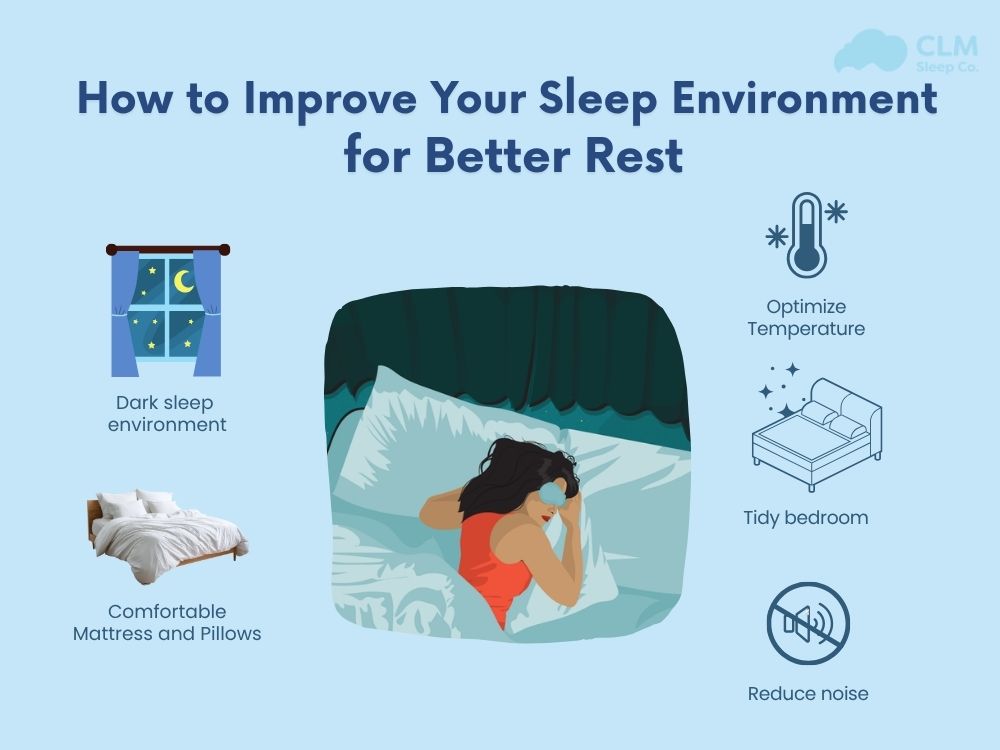
- Poor sleep environment (noise, light, uncomfortable mattress)
- Medical conditions such as chronic pain, depression, or hormonal imbalances
- Certain medications that suppress deep sleep, including some antidepressants or beta-blockers
How to Improve Deep Sleep
Improving deep sleep starts with good habits and a restful environment:
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule, going to bed and waking up at the same time daily.
- Exercise regularly, but avoid vigorous workouts close to bedtime.
- Take a warm bath or use heat before sleep to promote slow-wave sleep.
- Limit caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine, especially in the evening.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine like reading or gentle stretching.
- Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet for better sleep quality.
- Avoid screens and bright lights before bed to help melatonin production.
- If unable to sleep after 20 minutes, get up and do a calming activity until sleepy.
- Replace old pillows or mattresses to ensure comfort.
When to See a Doctor
If you have ongoing trouble getting sleep or experience symptoms like daytime fatigue, trouble focusing, or loud snoring, it’s time to see a specialist.
CLM Sleep offers sleep tests, diagnosis, and personalized treatment to help improve your sleep quality. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and take control of your sleep health.
Conclusion
Deep sleep is a non-negotiable part of a healthy life. It fuels your physical recovery, mental clarity, emotional stability, and immune strength. If you’re waking up tired, feeling foggy, or battling mood swings, the root cause could be poor sleep quality. Prioritize your deep sleep – and if needed, seek help. CLM Sleep is here to guide you with expert care, testing, and treatment options tailored to your unique sleep needs. Because better sleep starts with deeper sleep.